Principle of Hammer Mill: It is a size reduction equipment where stresses of varied nature are applied to achieve size reduction. Term size reduction is a process in which particles of solid are broken or cut into smaller pieces using mechanical stress. Hammer mill works on the principle of impact between rapidly moving hammers mounted on a motor and the material to be milled. As the hammers revolve at peripheral speeds reaching 10 m.s-1, they direct themselves towards the radial directions and hit the dropping feed breaking its particles into small fragments.
Construction of Hammer Mill:
The construction of the hammer mill is shown in the illustration below. This construction can either be of vertical or horizontal shaft type. This article discusses the horizontal type of mill often used in the industry. A typical hammer mill consists of a hopper, horizontal shaft, rotor, hardened steel or stainless-steel hammers, and removable.
- Hammers are usually made of hardened steel or stainless steel with an impact surface of extremely abrasive material such as haystellite and carbaloy; however, pharmaceutical use hammers are made of stainless steel SS316.
- Hammers are made of two shapes; bar-shaped or stirrup-shaped; where bar-shaped hammers are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Depending on the purpose, the edges of the hammers can be either flat, sharp or both on each side. Hammers may be of swing or rigid type.
- Usually, free swing-type hammers have an advantage over rigid ones in that there will be an increased clearance between the hammer and the screen. This increased clearance helps to overcome excessive build occurring in the mill.
- Hammers are pinned to a rotor disk, and this disk is mounted on a single horizontal shaft. Several such rotor disks carrying 4 to 8 hammers are mounted on the central shaft in a conventional hammer mill. The diameter of the rotor disk ranges from 150mm to 250mm.

You might want to read these:
Working of Hammer Mill:
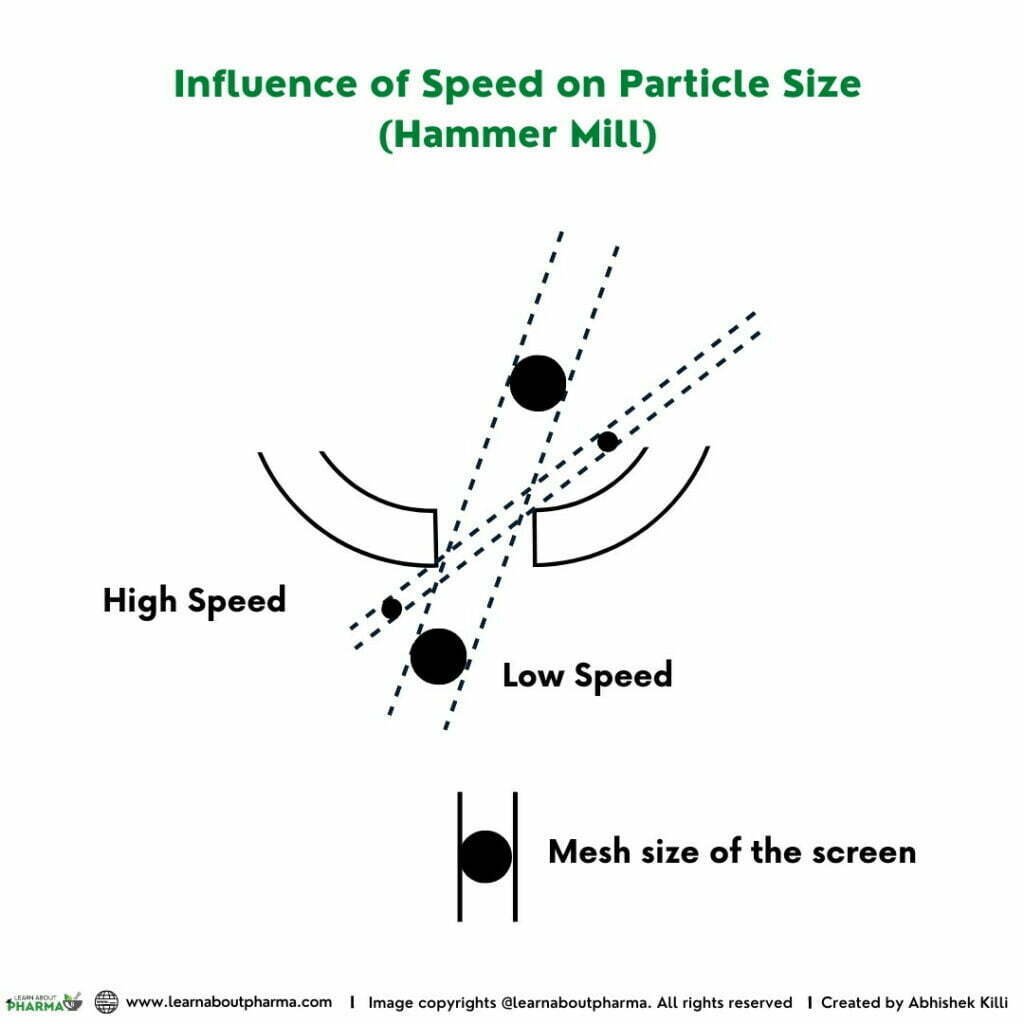
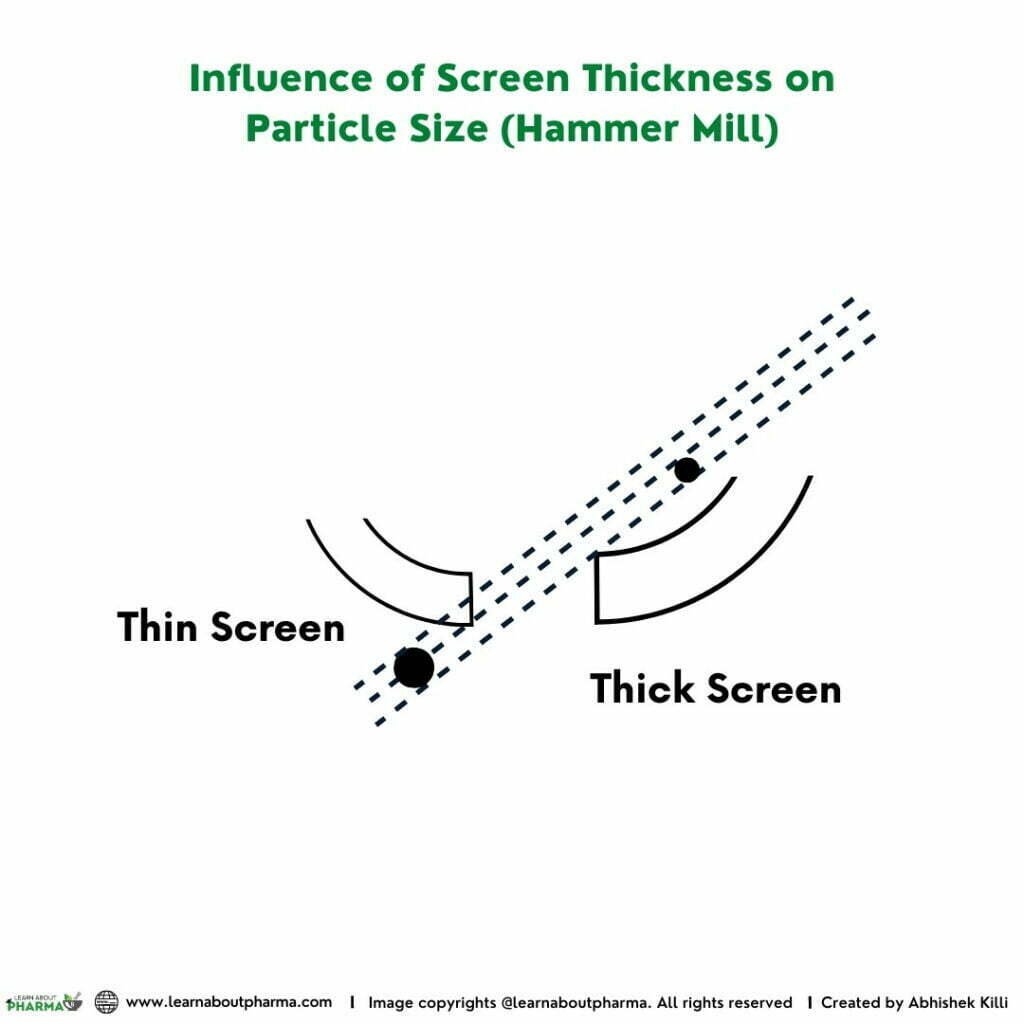
The shaft is rotated at high speed in continuous motion between 6000 to 15000 rpm. The material is fed from the top of the casing vertically through the hopper and is passed into the milling chamber while the hammers are in continuous motion. The rotating hammers beat the material to yield smaller particles. These particles then pass through the screen holes. Since the particles exit the holes tangentially, the size of the particles is considerably smaller than the holes (Refer to the figure below). A Hammer mill operating under lower speed generates larger-sized particles than the mill operating at high speed. Similarly, the screen thickness influences the size of the particles exiting the screen apertures. Under constant milling speed, the size of particles exiting the thicker screen is smaller when compared to the ones from the thin screen. (Refer to the figure below).
The fineness of the particles can further be regulated by altering the following:
- Rotor speed
- Feed rate
- Clearance between the hammers and the screen.
- Number of hammers on rotor
- No of rotors attached to a shaft.
- Type of hammers used
- Screen size
Screens used in the hammer mill are always interchangeable and can be changed based on the particle size requirement. Since the mill operates with great speed, much heat gets generated; however, hammers act as centrifugal fans where large amounts of air are drawn through the mill. In most cases, this is sufficient to counteract the heat generated.
Advantages of Hammer Mill:
- Hammer mill is easy to install, operate, dismantle and clean up.
- It occupies less space and can be easily placed in one corner of the manufacturing area.
- Various grades of material can be handled using screens of different sizes.
- It is versatile, and speed and screens can rapidly change based on milling requirements.
- Scale-up problems are minimal, provided the same type of mill is used.
- Operational costs are minimal while processing materials using a Hammer mill.
- As milling operation is carried out under closed conditions, dust generated can be reduced, and explosion hazards can be prevented.
- Hammer mill produces particles of varied size distribution with a minimum of fines.
Disadvantages of Hammer Mill:
- Milling operation involves heat build-up, so product deterioration is possible in a few cases.
- Milling of abrasive materials could make the screens and hammers susceptible to wear and damage.
- Low melting sticky, fibrous and hard materials are not suitable for milling operation. It might result in mill fouling due to heat generation.
- An uncontrolled feed rate could choke the mill, leading to damage.
- Screen clogging with process material is the most common problem encountered in milling.
Pharmaceutical uses of Hammer mill:
- Used to process wet and dry granulation process materials and also disperse powder mixtures
- Used in milling pharma API, excipients like sugar and herbal medicine
- Hammer mill is used to powder barks, leaves and roots of medicinal plants.



