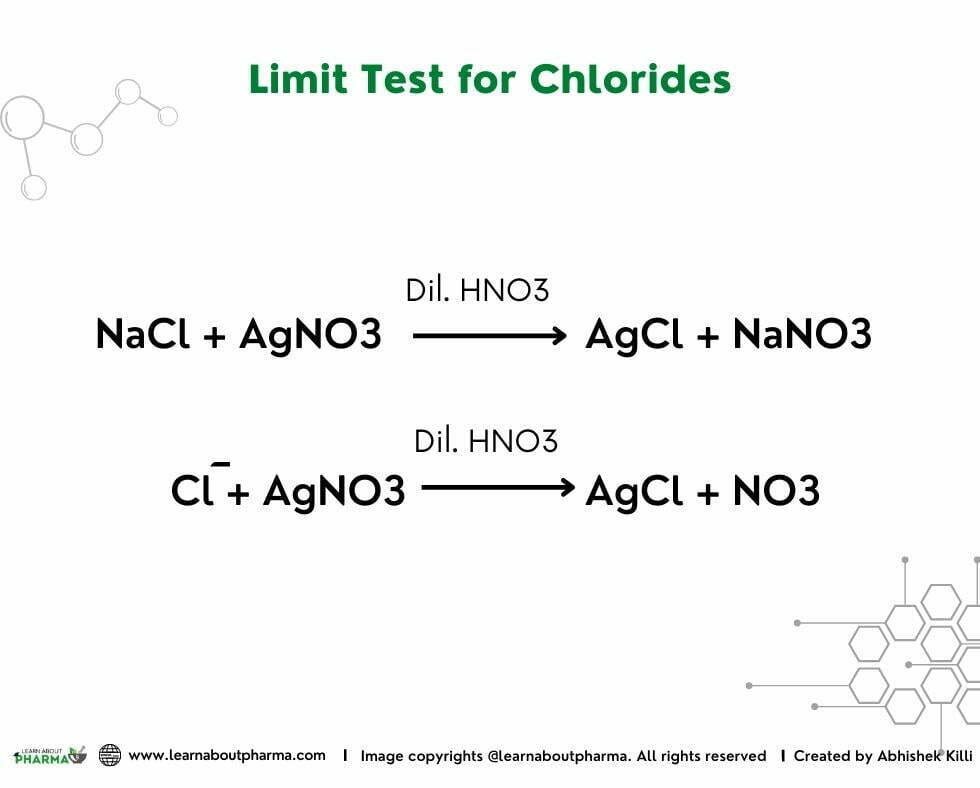
Limit test for Chloride is based on the reaction of soluble chloride with silver nitrate in presence of dilute nitric acid to form silver chloride, which appears as opalescence/turbidity in the solution.
Definition of Limit Test:
Limit tests are quantitative or semi-quantitative tests designed to identify, distinguish and control small quantities of impurities that are likely to be present in the pharmaceutical substance and to prevent their adverse effects. These tests are carried out to detect minute impurities in an unknown substance by comparing it with a standard. These impurities exhibit a specific reaction with some reagents used in the test.
Principle of Limit test for Chloride:
Limit test for Chloride exhibits a silver chloride precipitate upon the reaction of soluble chloride ions with silver nitrate in the presence of dilute nitric acid. This reaction makes the test solution turbid, and the extent of turbidity/opalescence depends on the amount of Chloride in the sample. The sample turbidity is finally compared with turbidity/opalescence produced by the standard solution.
Aim:
The aim of this experiment is to carry out the limit tests for Chloride in the given samples.
Apparatus:
Nessler’s cylinder, Glass rod, and Analytical balance.
Chemicals:
Dilute Nitric Acid (HNO3), Silver nitrate (AgNO3), and Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Procedure:
To perform a limit test for Chloride, a standard and test solution is required. Let us know the preparation of these solutions. Take two Nessler’s cylinder and name one as “test” and the other as “standard.”
- Preparation of test solution:
Accurately measure the known amount of sample as directed in the pharmacopeia and dissolve it in 15ml of distilled water. Transfer this 15ml prescribed solution into a Nessler’s cylinder labeled “test.” Continuously stir the solution and slowly add 1ml dilute nitric acid to it. Add 1ml silver nitrate reagent to this solution and make up the volume of the Nessler’s cylinder to 50ml with distilled water. Stir the solution and keep it aside for 5 minutes, protected from light.
You might want to read these:
Preparation of Standard solution:
The standard solution shall be prepared in the same manner as the test solution. Take a Nessler’s cylinder; add 10ml of chloride standard solution (25ppm Cl), and dilute it with 10 ml of distilled water. Slowly mix the solution, add 1ml dilute nitric acid, and make up the volume of the Nessler’s cylinder up to 50ml with distilled water. Stir the solution and keep it aside for 5 minutes, protected from light.
Observation:
After standing for 5 min protected from light, examine the tubes laterally against a black background. Any opalescence observed in the test solution is less intense than in the standard. If opalescence in the test solution is less than the standard solution, the test solution is said to pass the limit test for Chloride and vice-versa.
Information:
- Chloride standard solution (25 ppm Cl): Dilute 5 mL of 0.0824% w/v solution of sodium chloride to 100 mL with distilled water.
- Dilute nitric acid: Dilute 1.06 mL of concentrated nitric acid in sufficient distilled water to produce 100ml.
- 0.1M Silver nitrate: Dissolve 1.7 g of silver nitrate to 100 mL with distilled water.